...
![]() Attribute Extensions are much slower and less efficient than native columns e.g. when filtering. Use them sparingly and cautiously!
Attribute Extensions are much slower and less efficient than native columns e.g. when filtering. Use them sparingly and cautiously!
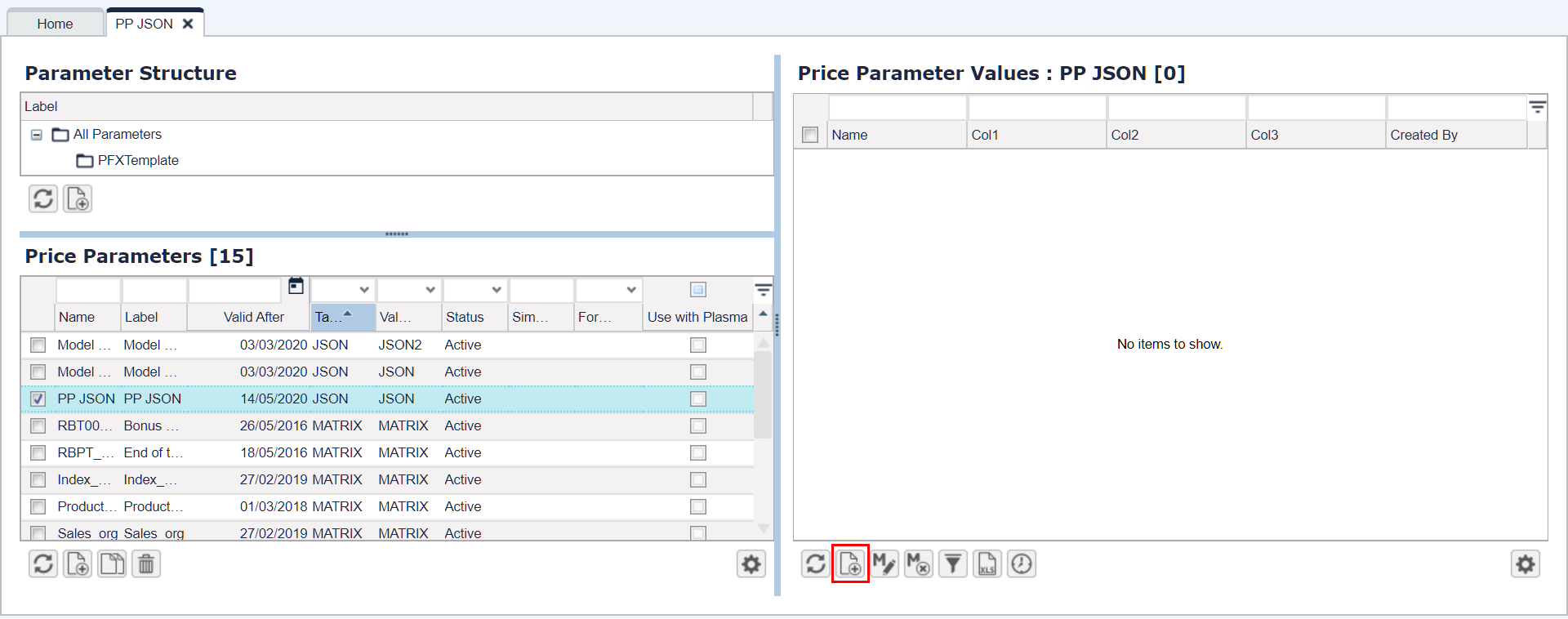
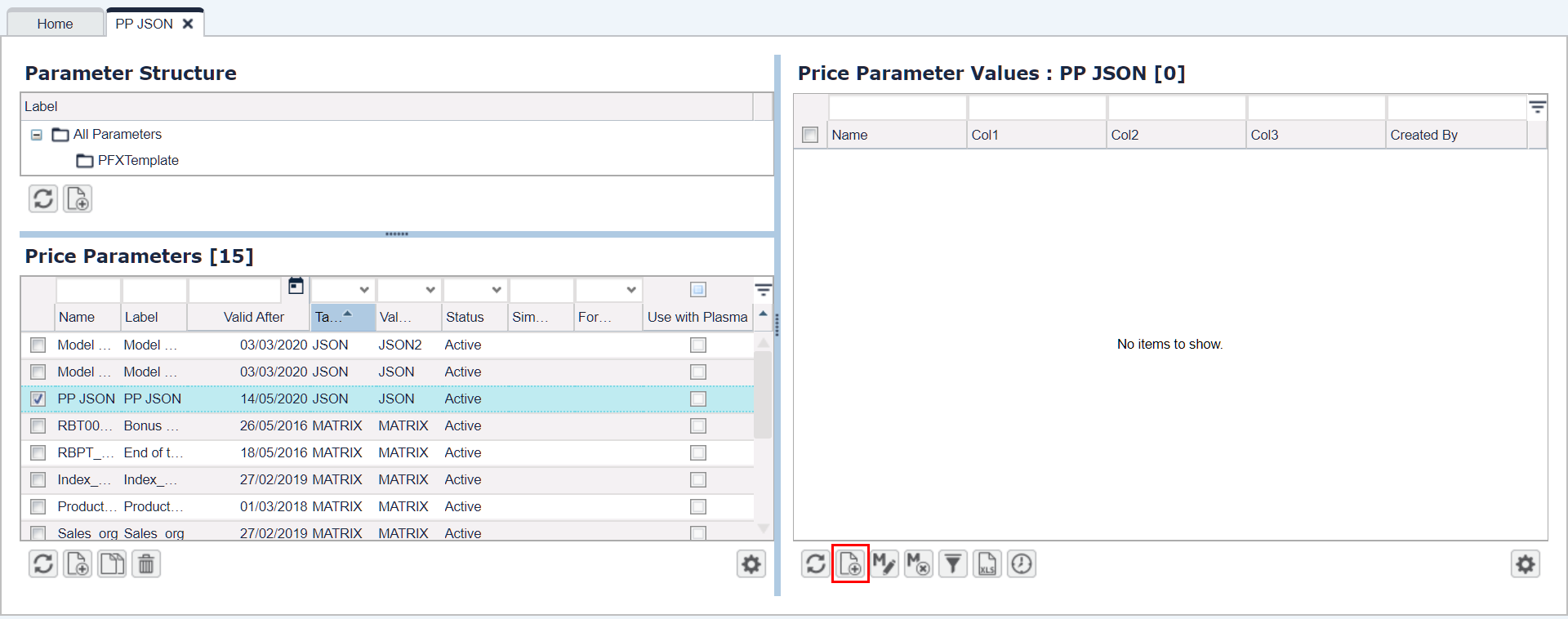
Go to Company Parameters and create a new one.
Fill in the mandatory fields in the PP table.
As 'Table Type' select JSON; as 'Value Type' select JSON or JSON2 depending on whether you want to have one or two key columns.Select the newly added PP and proceed to the right pane with Company Parameters Values.
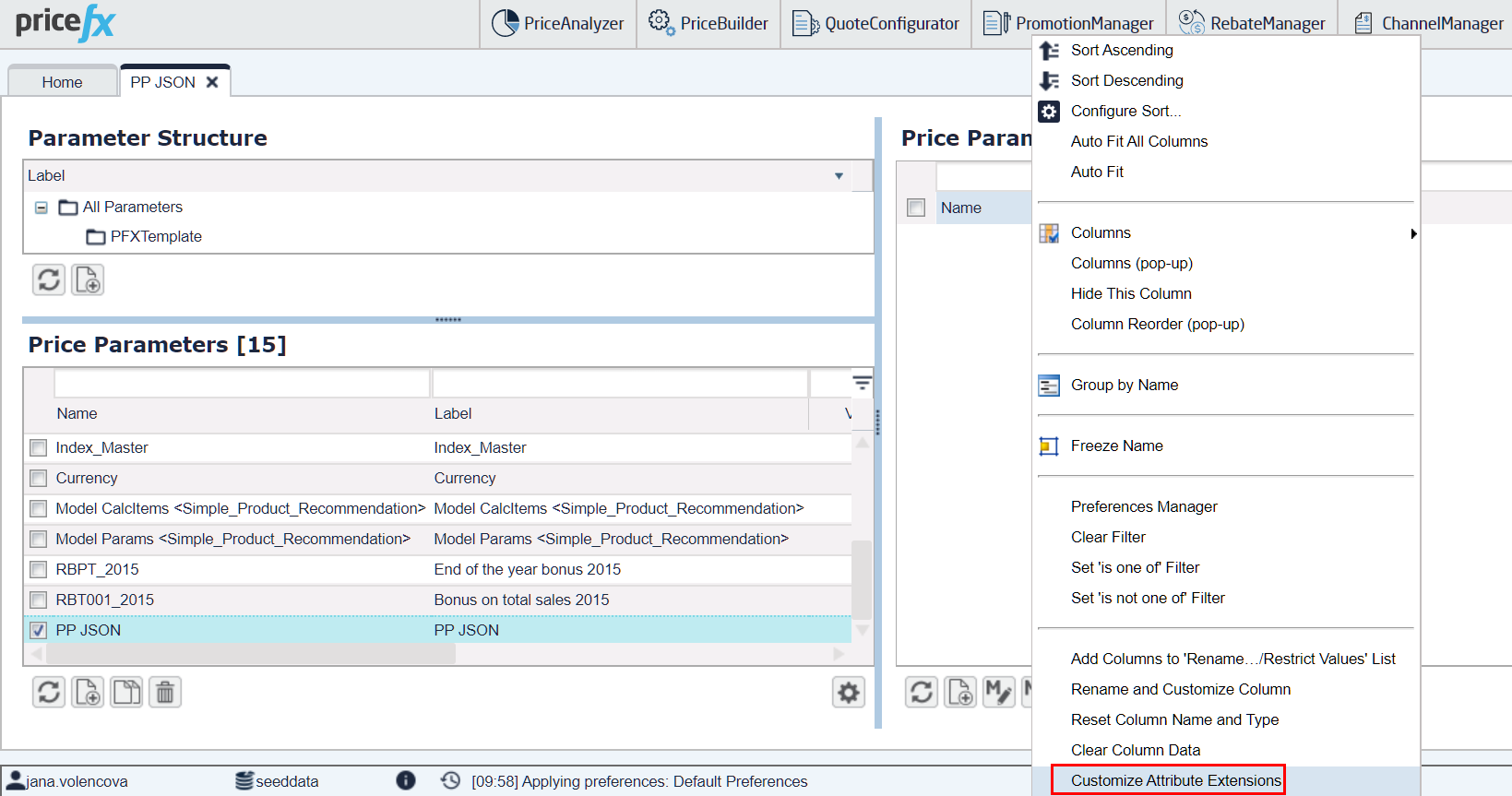
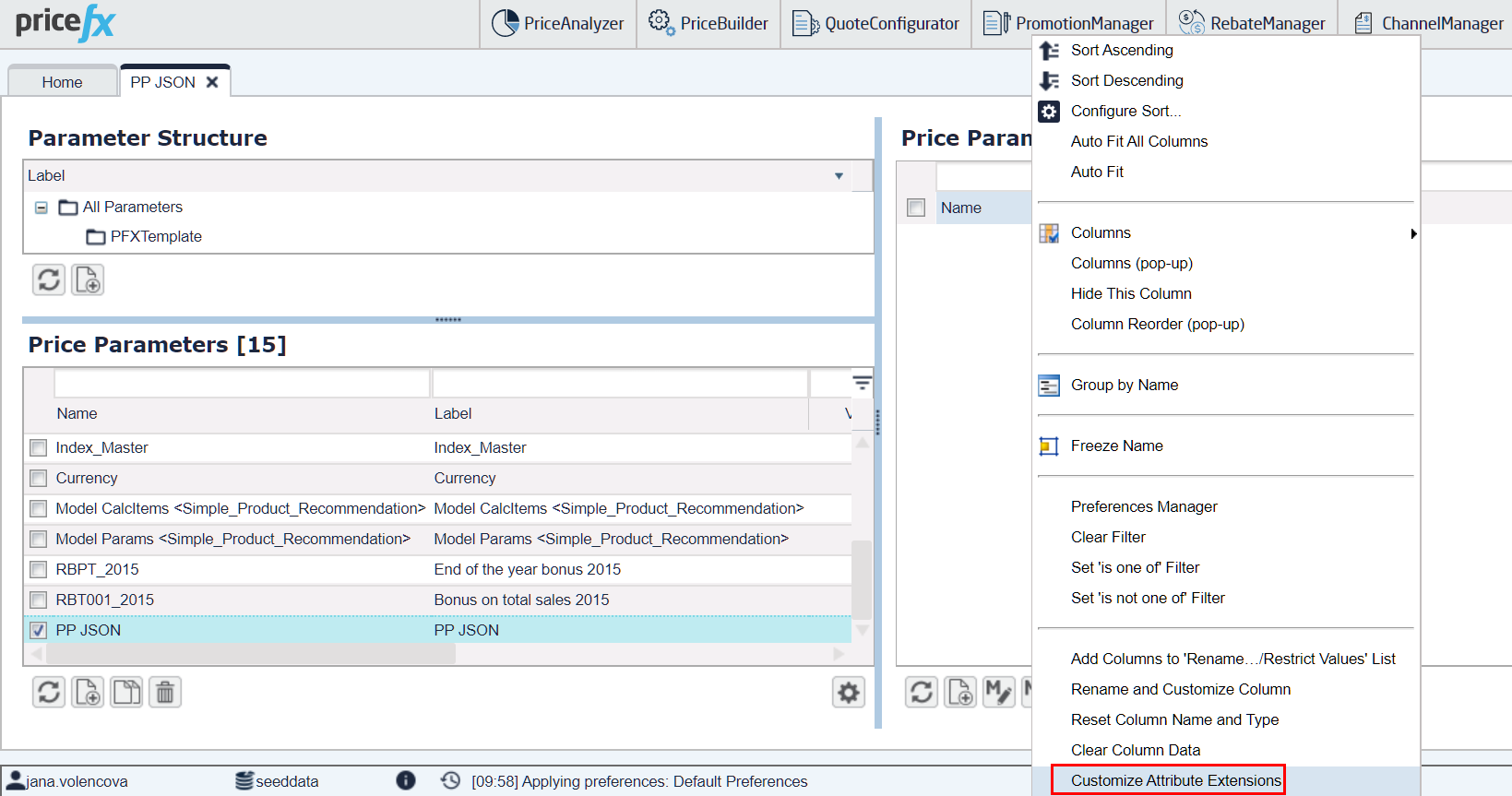
Click the table header and select 'Customize Attribute Extensions' from the context menu.
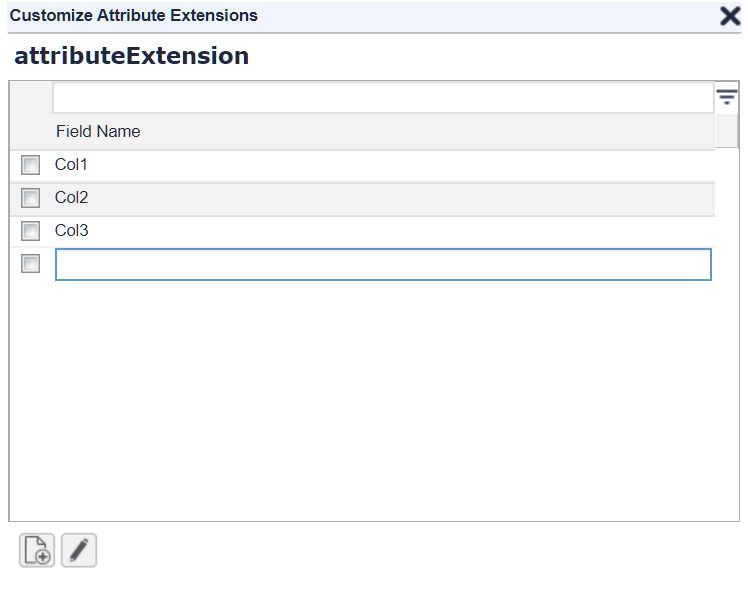
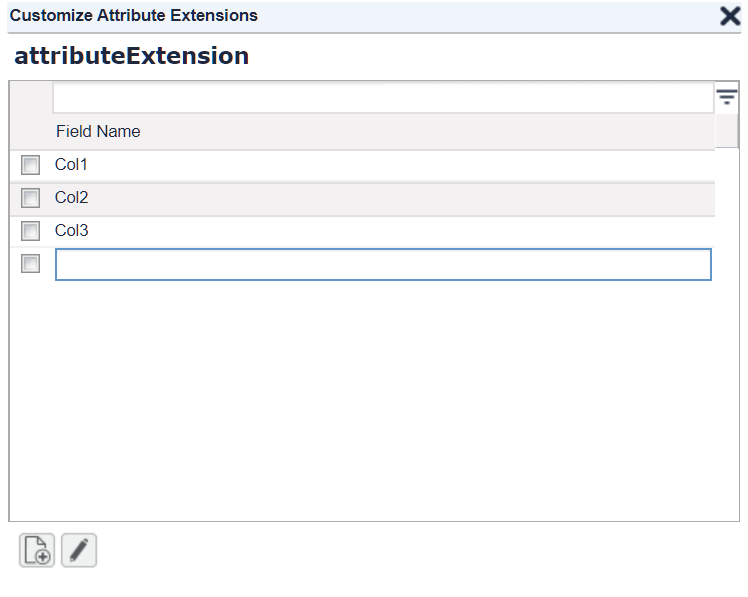
In the popup dialog create new columns.
Close the dialog. (Your entries will be saved.)
To see the new columns in the Company Parameter Values table, click elsewhere in the table (e.g. a different Company Parameter).
Go back to your Company Parameter and the table on the right will be updated.
Add the Company Parameters values in the table.
Examples
As mentioned above, all special columns are saved in one column called "attributeExtension".
For the JSON table, the key is the column "name".
For JSON2, there are two keys "key1" and "key2".
Fetch
Querying data is similar to a Company Parameter table.
JSON:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
def filter = Filter.equal('name', key)
def data = api.findLookupTableValues(<table_name>, filter)
data.each {row ->
row.attributeExtension___<name of special column1> //three underscores
row.attributeExtension___<name of special column2>
…
} |
In case of JSON2, there is a filter:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
def filter = Filter.and(Filter.equal('key1', key1),Filter.equal('key2',key2) |
...
To save one record:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
String key = 'my_key' //creates map where each attribute is name of the special column def attributeExtension = [ <name_of_special_column1> : <value1>, <name_of_special_column2> : <value2> ] //creates structure for the insert command, tableId is the ID of the JSON table – you need to find it out def req = [data: [ header: ['lookupTable', 'name', 'attributeExtension'], //for JSON2 use ['lookupTable', 'key1', 'key2', 'attributeExtension'] data : [[tableId, key, api.jsonEncode(attributeExtension)]] ]] //encodes the inserted structure def body = api.jsonEncode(req) def result = api.boundCall( 'customerA', //partition name '/loaddata/JLTV', //for JSON2 table it is JLTV2 body, true) |
...